 Our Recent Programs
Our Recent Programs
Sericulture Research
Food Science and Nutrition
Livestock Feeds and Nutrition
Soil Fertility and Health Management
Agricultural Economics
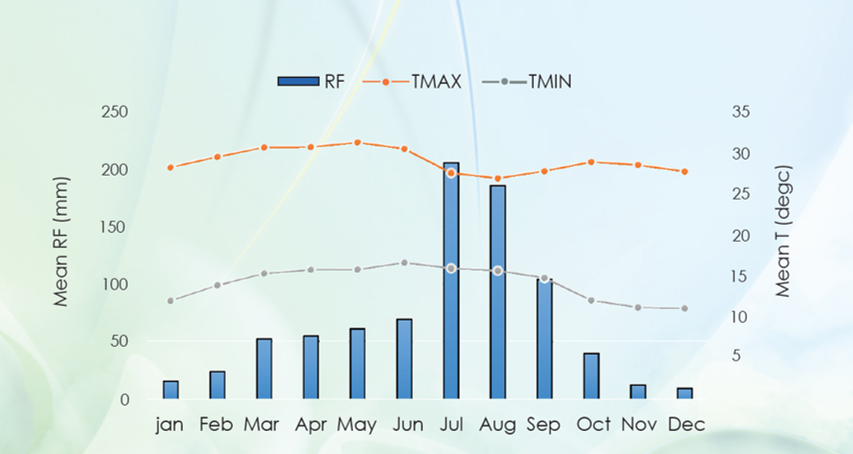
Climate and Geospatial
- Parasitic weeds (Orobanche ramosa L., Striga asiatica, Striga hermonthica),
- Sedges (Cyperus rotundus, Cyperus esculentus),
- Grass weeds (Digitaria ternata, Digitaria abyssinica, Cynodon dactylon, Sorghum arundenanceum, Echinocloa colona)
- Broad-leaved weeds (Launea cornuta, Portulaca oleracea, Tribulus teresteris, Commelina benghalensis, Parthenium hysterophorus, Xanthium abyssinicum, Datura stramonium, Tagetes minuta, Galinsoga parviflora Cav., Amaranthus hybridus, Guizotia scabra and Argemone mexicana).
Agricultural Entomology
Since then, entomological research activities on the mandate crops of MARC including warm season vegetables, tropical and subtropical fruits, tall cereals (sorghum and maize), and lowland pulses mainly common bean have been conducted. Insect pest survey, crop loss assessment and management studies have been conducted on key insect pests of these crops.
Read More







.jpg)

.jpg)

.jpg)
.jpg)



.jpg)











